Artificial Intelligence (AI) powers the systems that assist us daily—from self-driving cars to chatbots and smart home devices. At the heart of these technologies lie AI agents, software entities that perceive their environment and take actions to achieve specific goals. But did you know there are exactly 5 types of AI agents based on their complexity and capabilities?
In this 100% human-written, SEO-optimized guide, we’ll explain the 5 types of AI agents, how they work, and real-world examples to make these concepts easy to understand.
📦 What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are autonomous entities that:
✅ Sense their environment through inputs like sensors or data streams
✅ Process information using logic or AI models
✅ Act to influence their surroundings or solve problems
They range from simple rule-based systems to advanced learning agents that adapt over time. Understanding the 5 types of AI agents helps businesses, developers, and AI enthusiasts choose the right approach for different applications.
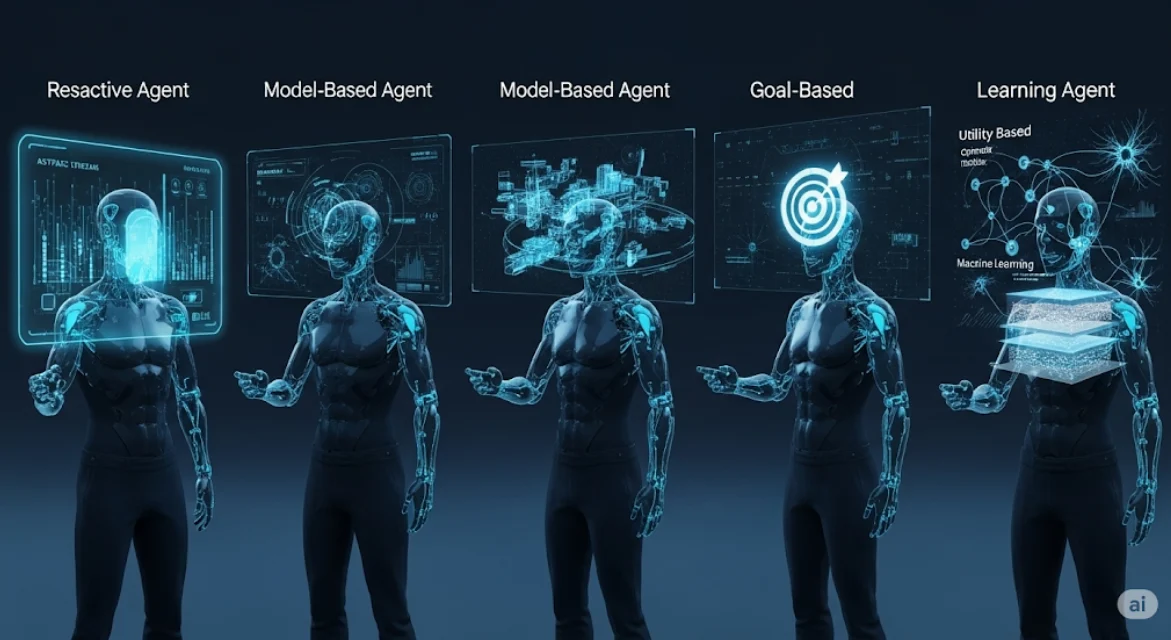
🔍 Overview: The 5 Types of AI Agents
The five categories are:
1️⃣ Simple Reflex Agents
2️⃣ Model-Based Reflex Agents
3️⃣ Goal-Based Agents
4️⃣ Utility-Based Agents
5️⃣ Learning Agents
Let’s explore each type in detail to understand their features, functions, and use cases.
1️⃣ Simple Reflex Agents
Definition: These AI agents react directly to environmental stimuli based on predefined rules, without memory or internal modeling.
How They Work:
Perceive current state
Match to condition-action rule (e.g., IF traffic light is red THEN stop)
Execute corresponding action
Example Use Cases:
🚦 Traffic light control systems
🧹 Basic robot vacuums (clean if dirt detected)
💡 Motion-sensor lights
Advantages:
✔️ Simple to design
✔️ Fast response
✔️ Reliable for predictable tasks
Limitations:
❌ Can’t handle complex, unseen scenarios
❌ No adaptability
Summary: Ideal for repetitive, rule-driven environments but limited to basic operations.
2️⃣ Model-Based Reflex Agents
Definition: These agents maintain a basic internal model of their environment to make more informed decisions.
How They Work:
Track past states using memory
Update internal model (e.g., map of surroundings)
Use rules combined with environmental context to act
Example Use Cases:
🏠 Smart home devices adjusting based on usage patterns
🤖 Warehouse robots navigating spaces
🛰️ Drones monitoring delivery routes
Advantages:
✔️ Better decision-making than simple agents
✔️ Can operate in partially unknown environments
Limitations:
❌ Still rule-dependent
❌ Limited long-term learning
Summary: A step up from reflex agents, suitable for moderately dynamic settings.
3️⃣ Goal-Based Agents
Definition: These agents pursue specific objectives, selecting actions that help them achieve defined goals rather than simply reacting.
How They Work:
Maintain internal goals (e.g., reach destination)
Evaluate possible actions based on goal achievement
Use search algorithms and planning
Example Use Cases:
🚗 Self-driving cars plotting safe routes
🧭 Virtual assistants scheduling meetings
🎮 Game AI navigating toward objectives
Advantages:
✔️ More flexible than rule-based systems
✔️ Focus on achieving desired outcomes
Limitations:
❌ Requires clear goal definition
❌ May need complex decision trees
Summary: Excellent for complex tasks with clear goals, but requires goal engineering.
4️⃣ Utility-Based Agents
Definition: These agents assess the utility—or value—of outcomes, selecting actions that maximize overall satisfaction or benefit.
How They Work:
Evaluate different action consequences
Assign utility scores to each option
Choose actions with highest expected utility
Example Use Cases:
💰 Stock trading bots optimizing profit vs. risk
🏢 Smart building systems balancing comfort and energy use
🛒 E-commerce recommendation engines
Advantages:
✔️ Handles trade-offs effectively
✔️ Optimizes for user-defined preferences
Limitations:
❌ Requires accurate utility models
❌ May struggle with uncertain environments
Summary: Ideal for scenarios needing optimization or balancing multiple factors.
5️⃣ Learning Agents
Definition: The most advanced of the 5 types of AI agents, these systems improve performance through experience and adaptation.
How They Work:
Use machine learning to analyze outcomes
Update models based on feedback
Continuously refine decision-making
Example Use Cases:
🧠 ChatGPT and conversational AI evolving with user interactions
🚀 Autonomous vehicles learning new routes
🔍 Predictive maintenance in factories
Advantages:
✔️ Adapt to changing environments
✔️ Learn complex patterns
✔️ Improve over time
Limitations:
❌ Requires large data inputs
❌ Potential for unintended behavior without oversight
Summary: Best for dynamic, evolving tasks requiring continual improvement.
🎯 Quick Comparison Table
| Agent Type | Memory | Goal Awareness | Adaptability | Example Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Reflex Agent | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | Motion sensors, basic robots |
| Model-Based Agent | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No | Smart vacuums, drones |
| Goal-Based Agent | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | Self-driving cars, virtual assistants |
| Utility-Based Agent | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ Limited | Trading bots, smart thermostats |
| Learning Agent | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | Chatbots, autonomous vehicles |
🏢 Real-World Benefits of the 5 Types of AI Agents
Automation: From basic tasks to complex decision-making
Efficiency: Speed and accuracy improvements
Cost savings: Reduced need for human intervention
Scalability: AI agents can serve thousands simultaneously
Personalization: Tailor experiences based on user data
By selecting the appropriate type, businesses optimize AI deployment across different functions.
🌟 Choosing the Right AI Agent for Your Needs
When deciding among the 5 types of AI agents, consider:
✅ Task complexity – Simple reflex for basic, repetitive work
✅ Environment dynamics – Model-based for evolving conditions
✅ Goal specificity – Goal-based for clear outcomes
✅ Optimization needs – Utility-based for trade-offs
✅ Learning demands – Learning agents for adaptation
Combining types is also possible—many AI systems integrate multiple agent capabilities for better results.
🔮 Future Trends: AI Agents Evolving
The future of AI agents includes:
🚀 More autonomous learning across industries
🔗 Multi-agent collaboration for complex tasks
🤖 AI agents in healthcare, law, education, and defense
🌍 Ethical AI ensuring transparency and fairness
🧠 Hybrid agents blending all five types for versatility
Understanding the 5 types of AI agents lays the groundwork for embracing these innovations.
🔗 Related Reads You Might Like:


Pingback: How Does an AI Agency Work? Complete Guide for Businesses in 2025 - Trade Pluse Ai